Description
Epithalon Peptide for sale
Disclaimer: This content summarizes research literature only. It makes no therapeutic claims, no medical recommendations, and is provided strictly for research and educational purposes.

What Is Epithalon?
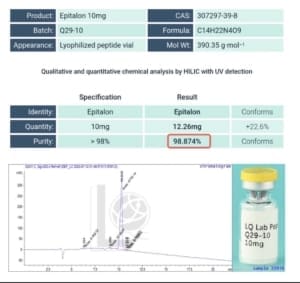
Epithalon (also called Epitalon or Epithalamin) is a synthetic tetrapeptide with the sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly. It was originally derived from research on pineal peptides and has been studied in the context of cellular senescence and telomerase activation. We offer a variety of strengths regarding epithalon peptides for sale also sometimes called Epitalon Peptide. Also, check out this interesting article regarding Epithalon vs NAD+.

Chemical Structure
Epithalon is a short peptide composed of four amino acids:
- Ala – Alanine
- Glu – Glutamic acid
- Asp – Aspartic acid
- Gly – Glycine
Its small size contributes to stability and the ability to interact with regulatory pathways at the cellular level. It has been investigated as part of studies on aging biology and genome stability.
Mechanistic Insights from Research
Laboratory studies have reported that Epithalon may influence cellular mechanisms such as:
- Telomerase Activity: Research indicates Epithalon can stimulate telomerase in human somatic cells, potentially contributing to telomere elongation in vitro.
- Oxidative Stress Modulation: Some preclinical studies suggest effects on antioxidant systems and cellular homeostasis.
These findings remain preliminary and are primarily limited to in vitro and preclinical studies.
Selected Research References
- Khavinson V et al. Epithalamin induces telomerase activity in human somatic cells. PubMed 10833828.
- Anisimov VN et al. Pineal peptide Epithalon prolongs life span in rats. PubMed 11121901.